[Olson, 1967]
Definitions of Sound
Question:
If a tree falls in the forest, and there is no one to hear it, will there be a sound?...
This is a very old philosophical dilemma which relies on using the word "sound" for two different purposes. One use is as a description of a particular type of physical disturbance:
"Sound is an organised movement of molecules caused by a vibrating body in some medium - water, air, rock or whatever."[*]
The other is as a description of a sensation:
"Sound is the auditory sensation produced through the ear by the alteration ... in pressure, particle displacement, or particle velocity which is propagated in an elastic medium."[#]
Both these definitions are correct, they differ only in the first being a cause and the second being an effect.
The Nature of a Sound Wave
Sound originates when a body moves back and forth rapidly enough to send a coursing
wave through the medium in which it is vibrating.
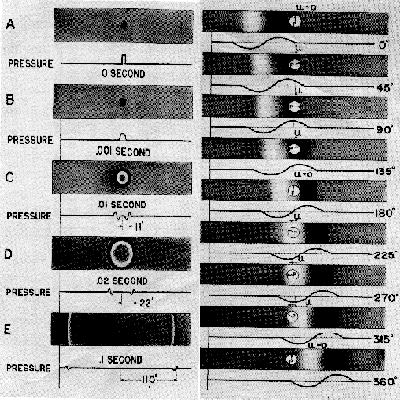
Demonstration:
A simple form of sound wave is produced by an explosion of a small balloon of compressed
air. By bursting the balloon, potential energy (energy of position) is converted
to kinetic energy (energy of motion).
Select the "WAVE" link to see the animated wave front. WAVE
This is a spherical wave. It consists of one condensation and one rarefaction. The wavefront is a continuous spherical surface in which the variations for all parts of the surface have the same phase.